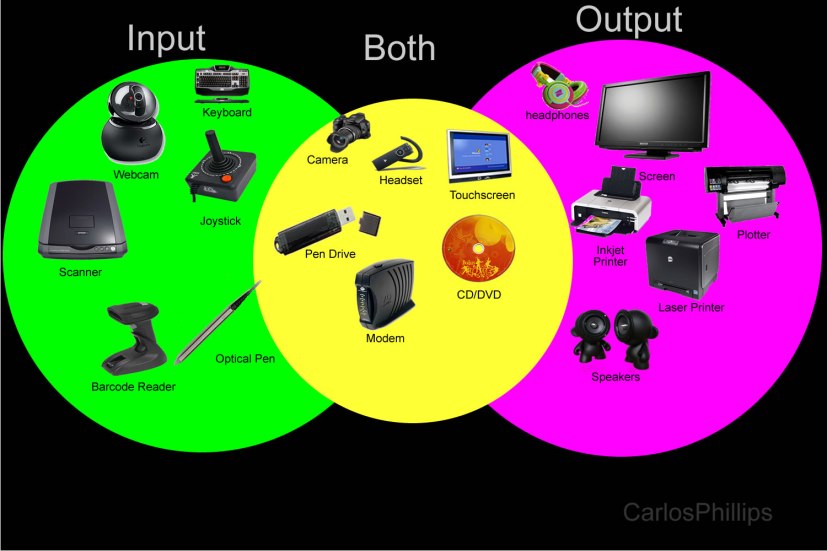
Input & Output
- Input hardware consists of devices that translate data into a form the computer can process. an input device is a peripheral (piece of computer hardware equipment) used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system such as a computer or other information appliance. Examples of input devices include keyboards, mouse, scanners, digital cameras and joysticks. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Input_device
- Output hardware consists of devices that translate information processed by the computer into a form that humans can understand.
An output device is any piece of computer hardware equipment used to communicate the results of data processing carried out by an information processing system (such as a computer) which converts the electronically generated information into human-readable form. An output device is any piece of computer hardware equipment used to communicate the results of data processing carried out by an information processing system (such as a computer) which converts the electronically generated information into human-readable form. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Output_device
Input Hardware
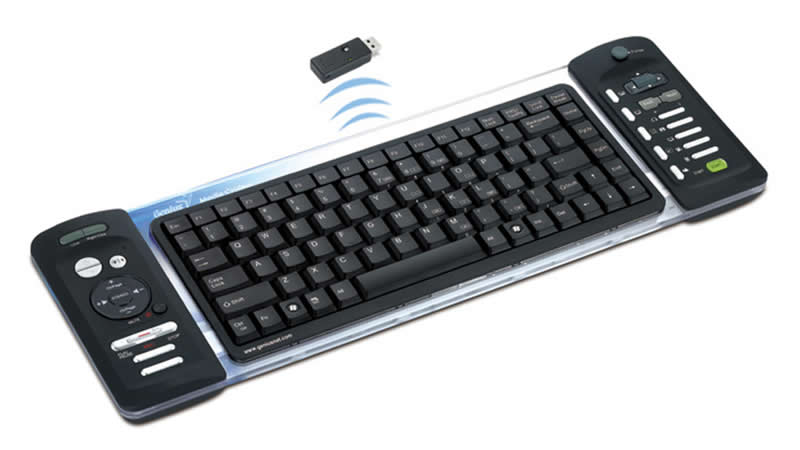 Keyboards
Keyboards
– is a device that converts letters, numbers, and other characters into electrical signals that can be read by the computer’s processor. A typewriter-style device, which uses an arrangement of buttons or keys, to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_keyboard
- Specialty keyboards and terminals
- Dumb terminals also called a video display terminal (VDT), has a display screen and a keyboard and can input and output but cannot process data
- An Intelligent terminal has its own memory and processor, as well as a display screen and keyboard
- AN Internet terminal provides access to the internet
Pointing Devices
– control the position of the cursor or pointer on the screen and allow the user to select opinions displayed on the screen. An input interface (specifically a human interface device) that allows a user to input spatial (i.e., continuous and multi-dimensional) data to a computer. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pointing_device
- The mouse and its variants—trackball, pointing stick, and touchpad
- Mouse a device that is rolled about on a desktop mouse pad and directs a pointer on the computer’s display screen
- Trackball is a movable ball, mounted on top of a stationary device, that can be rotated using fingers or palm
- Pointing stick looks like a pencil eraser protruding from the keyboard between the G, H, and B keys. When you move the pointing stick with your finger, the screen pointer moves accordingly
- Touchpad is a small, flat surface over a which you slide your finger, using the same movements as you would with a mouse
- Touch screen is a video display that has been sensitized to receive input from the touch of a finger
- Pen Input: pen-based system, light pens, and digitizers
- Pen-based computer systems allows users to enter handwritting and marks onto a computer screen by means of a penlike stylus rather than by typing on a keyboard
- Light pen is a light-sensitive penlike device that uses a wired connection to a computer terminal
- Digitizer uses an electronic pen or a mouselike copying device called a puck that can convert drawings and photos to digital data
Scanning & Reading Devices
- Source data-entry devices create machine-readable data on magnetic media or paper or feed it directly into the computer’s processor
- Scanner or optical scanners, use light-sensing (optical) equipment to translate images of text, drawings, photos, and the like into digital form
- Resolution refers to the clarity and sharpness of an image and is measured in dots per inch (dpi)—the number of columns and rows of dots per inch. The higher the number of dots, the clearer and sharper the image
- Flatbed scanner or desktop scanner, which works much like a photocopier–the image being scanned is placed on a glass surface, where it remains stationary, and the scanning beam moves across it
- Bar-code readers:
- Bar codes are the vertical, zebra-striped marks you see on most manufactured retail products
- Bar-code readers are photoelectric (optical) scanners that translate the symbols in the bar code into the digital code
- Mark-recognition and character-recognition devices:
- Magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) is a character recognition system that uses magnetizable ink and special character
- Optical mark recognition (OMR) uses a special scanner that reads “bubble” marks and converts them into computer-usable form
- Optical character recognition (OCR) software converts scanned text from images (pictures of the text) to an editable text format (usually ASCII) that can be imported into a word processing application and manipulated
- Fax machines or facsimile transmission machine—scans an image and sends it as electronic signals over telephone lines to a receiving fax machine, which prints out the image on a paper
- Dedicated fax machines are specialized devices that do nothing except send and receive fax documents
- Fax modems is installed as a circuit board inside the computer’s system cabinet. It is a modem with fax capability that enables you to send signals directly from your computer to someone else’s fax machine or computer fax modem
Audio-Input Devices
- Audio-input device record analog sound and translates it for digital storage and processing
- Sound board is an add-on circuit board in a computer that converts analog sound to digital sound and stores it for further processing and/or plays it back, providing output directly to speakers or an external amplifier
- MIDI board pronounced “middie,” stands for “Musical Instrument Digital Interface“—uses a standard for the interchange of musical information between musical instruments, synthesizers, and computers
Webcams & Video-Input Cards
Webcam a video camera to a computer to record live moving images that can then be posted on a website in real time. A video camera that feeds or streams its image in real time to or through a computer to computer network. When “captured” by the computer, the video stream may be saved, viewed or sent on to other networks via systems such as the internet, and email as an attachment. When sent to a remote location, the video stream may be saved, viewed or on sent there. Unlike an IP camera(which connects using Ethernet or WI-Fi), a webcam is generally connected by a USB cable, or similar cable, or built into computer hardware, such as laptops. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Webcam
Digital Camera
– uses a light-sensitive processor chip to capture photographic images in digital form and store them on a small diskette inserted into the camera or on flash-memory cards. A camera that encodes digital image and videos digitally and stores them for later reproduction. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_camera
Speech-Recognition System
– using a microphone (or a telephone) as an input device, converts a person’s speech into digital signals by comparing the electrical patterns produced by the speaker’s voice with a set of prerecorded patterns stored in the computer. Is the translation of spoken words into text. It is also known as “automatic speech recognition” (ASR), “computer speech recognition”, or just “speech to text” (STT). http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Speech_recognition
Sensors
– is an input device that collects specific data directly from the environment and transmits it to a computer. A device that detects and responds to some type of input from the physical environment. The specific input could be light, heat, motion, moisture, pressure, or any one of a great number of other environmental phenomena. The output is generally a signal that is converted to human-readable display at the sensor location or transmitted electronically over a network for reading or further processing. http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/sensor
Radio-Frequency Identification Tags
– (RFID) tags are based on an identifying tag bearing a microchip that contains specific code numbers. These code numbers are read by the radio waves of a scanner linked to a database. A technology that uses electronic tags placed on objects, people, or animals to relay identifying information to an electronic reader by means of radio waves: a toll road equipped with an RFID payment system. dictionary.reference.com/browse/rfid
Human-Biology-Input Devices
Biometrics the science of measuring individual body characteristics. Biometric identifiers are often categorized as physiological versus behavioral characteristics. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biometrics
Output Hardware
- Softcopy is data that is shown on a display screen or is in audio or voice form; it exists only electronically. A soft copy (sometimes spelled “softcopy”) is an electronic copy of some type of data, such as a file viewed on a computer’s display or transmitted as an e-mail attachment. Such material, when printed, is referred to as a hard copy. http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/soft-copy
- Hardcopy is printed output. A printout of data stored in a computer. It is considered hard because it exists physically on paper, whereas a soft copy exists only electronically. http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/H/hard_copy.html
Traditional Softcopy Output: Display Screens
- Display screens also variables called monitors, CRTs, or simply screens—are output devices that show programming instructions and data as they are being output and information after it is processed
- Screen clarity—dot pitch, resolution, color depth, and refresh rate:
- Pixel for “picture elements,” is the smallest unit on the screen that can be turned on and off or made different shades
- Dot pitch (dp) is the amount of space between the centers of adjacent pixels; the closer the pixels, the crisper the image
- Resolution refers to the image sharpness of the display screen; the more pixels, or dots there are per square inch, the finer the level of detail
- Color depth or bit depth, is the amount of information, expressed in bits, that is stored in a dot
- Refresh rate is the number of times per seconds that the pixel s are recharged so that their glow remains bright
- Two types of monitors—CRT and flat panel:
- CRT (cathode-ray tube) is a vacuum tube used as a display screen in a computer or video display terminal
- Flat panel displays are made up of two plates of glass separated by a layer of a substance in which light is manipulated.
- One flat-panel technology is Liquid crystal display (LCD), in which molecules of liquid crystal line up in a way that alters their optical properties, creating images on the screen by transmitting or blocking out light
- Active-matrix versus passive-matrix flat-panel displays:
- Active-matrix display, also known as TFT (thin-film transistor) display, each pixel on the flat-panel screen is controlled by its own transistor
- Passive-matrix display, a transistor controls a whole row or column of pixels on the flat-screen display
- Color and resolution standard for monitors—SVGA, XGA, SXGA, UXGA, and QXGA:
- SVGA (super video graphics array) supports a resolution of 800 x 600 pixels, or variations, producing up to 16 million possible simultaneous colors
- XGA (extended graphics array) has a resolution of up to 1,024 x 768 pixels, with 65,536 possible colors
- SXGA (super extended graphics array) has a resolution of up to 1,280 x 1,024 pixels
- UXGA (ultra extended graphics array) has a resolution of up to 1,600 x 1,200 pixels and supports up to 16.8 million color
- QXGA (quantum extended graphics array) has a resolution of up to 2,048 x 1,536 pixels
Traditional Hardcopy Output: Printers
Printer is an output device that prints characters, symbols, and perhaps graphics on paper or another hardcopy medium. A peripheral which makes a persistent human-readable representation of graphics or text on paper or similar physical media. The two most common printer mechanisms are black and white laser printers used for common documents, and color ink jet printers which can produced high-quality photograph-quality output. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Printer_(computing)
The resolution, or quality of sharpness, of the printed image is indicated by dpi (dot per inch), which is a measure of the number of rows and columns of dots that are printed in a square inch. Indicates the resolution of images. The more dots per inch, the higher the resolution. A common resolution for laser printers is 600 dots per inch. This means 600 dots across and 600 dots down, so there are 360,000 dots per square inch. http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/D/dpi.html

- Impact printers: An impact printer forms character or images by striking a mechanism such as a print hammer or wheel against an inked ribbon, leaving an image on paper
- Nonimpact printers: Nonimpact printer form characters and images without direct physical contact between the printing mechanism and paper
- Laser printer creates images with dots. However, as in a photocopying machine, these images are produced on a drum, treated with a magnetically charged ink-like toner (powder), and then transferred from the drum to paper
- Laser printers run with software called a page description language (PDL). This software tells the printers how to lay out the printed page, and it supports various fonts
- Ink-jet printers spray onto a paper small, electrically charged droplets of ink from four nozzles through holes in a matrix at high speed
- Thermal printers used colored waxes and heat elements to produce images by burning dots onto special paper
- Plotters: A Plotter is a specialized output device designed to produce high-quality graphics in a variety of colors
- Multifunction printers—printers that do more than print: Multifuntion printers combine several capabilities, such as printing, scanning, copying, and faxing
Mixed Output: Sound, Voice, & Video
- Sound output: Sound-output devices produce digitized sounds, ranging from the beeps and chirps to music
- Voice output: Voice-output devices convert digital data into speech like sounds
- Video output: Video consists of photographic images, which are played at 15-29 frames per second to give the appearance of full motion
- Another form of video output is Videoconferencing, in which people in different geographic locations can have a meeting—can see and hear one another—using computers and communications
The Future of Input & Output



Towards More Source Data Automation
- Input help for the disabled
- More sophisticated touch devices
- Better speech recognition
- Smaller electronic cameras
- Pattern-recognition and biometric devices
- Brainwave devices
Towards More Realistic Output
- Display screens—better and cheaper
- Audio—higher fidelity
- Video—movie quality for PCs
- Three-dimensional output
Input & Output Technology & Quality of Life: Health & Ergonomics

Health Matters
- Repetitive stress injuries: Repetitive stress (or strain) injuries (RSIs) are wrist, hand, arm, and neck injuries resulting when muscle groups are forced through fast, repetitive motions. any of a group of debilitating disorders, as of the hand and arm, characterized typically by pain, numbness, tingling, or loss of muscle control and caused by the stress of repeated movements. dictionary.reference.com/browse/repetitive+strain+injury
- Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a debilitating condition caused by pressure on the median nerve in the wrist, producing damaged and pain to nerves and tendons in the hands. a median entrapment neuropathy that causes paresthesia, pain, numbness, and other symptoms in the distribution of the median nerve due to its compression at the wrist in the carpal tunnel. The mechanism is not completely understood but can be considered compression of the median nerve traveling through the carpal tunnel. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carpal_tunnel_syndrome
- Eyestrain and headaches:
- Computer vision syndrome (CVS) consists of eyestrain, headaches, double vision, and other problems caused by improper use of computer display screens. A temporary condition resulting from focusing the eyes on a computer display for protracted, uninterrupted periods of time. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_vision_syndrome
- Back and neck pains
- Electromagnetic fields:
- Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) are waves of electrical energy and magnetic energy. An electromagnetic field, sometimes referred to as an EM field, is generated when charged particles, such as electrons, are accelerated. All electrically charged particles are surrounded by electric fields. Charged particles in motion produce magnetic fields. http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/electromagnetic-field
- Noise
Ergonomics: Design with People in Mind
The purpose of ergonomics is to make working conditions and equipment safer and more efficient. A science that deals with designing and arranging things so that people can use them easily and safely. http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/ergonomics

REFLECTION:
I learned in these chapter 5 about the Hardware of Input and Output. These chapter 5 brings the meaning of input and output, input hardware, output hardware, the future of input and output, and input and output technology and quality of life of health and ergonomics. The most important part that I’ve learned in these chapter is knowing the ergonomics. Ergonomics means is the proper way to sit and using the laptop/computer properly. The tips of ergonomics of using the desktop helps my body feel relax and comfortable when using the laptop as browser for the internet.
